services
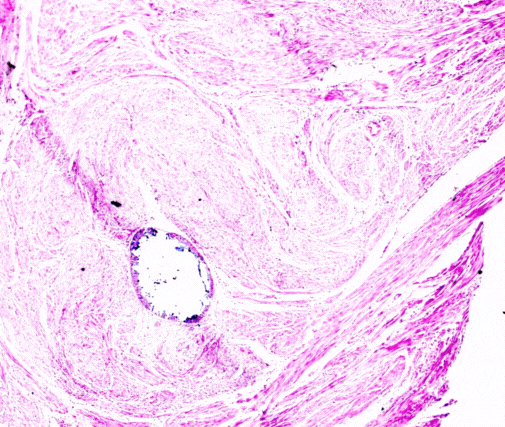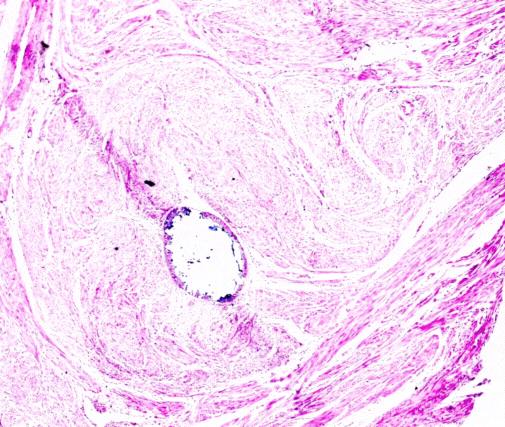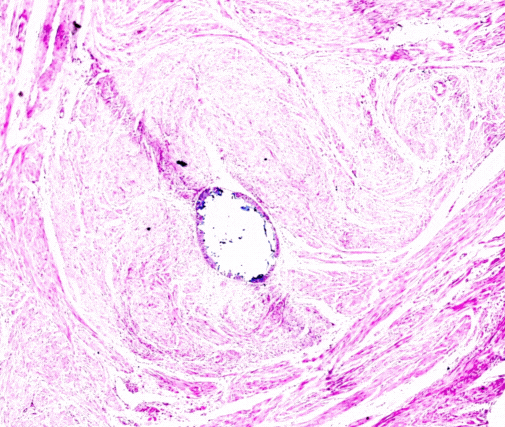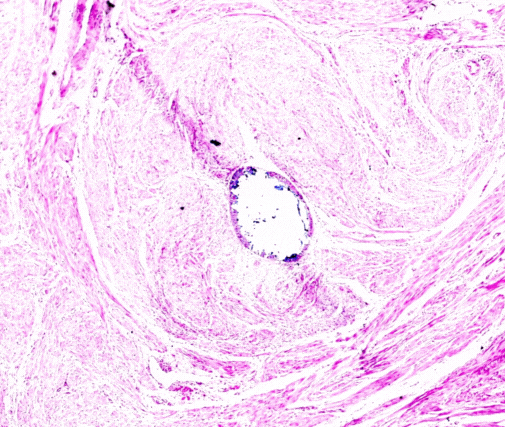
Renal biopsies are diagnostic procedures used to obtain a small sample of kidney tissue for examination under a microscope. This procedure helps nephrologists and pathologists assess kidney health, identify the cause of kidney diseases or abnormalities, and determine the best treatment approach. Key aspects of renal biopsies include:
Renal biopsies are performed when there is suspicion of kidney disease, unexplained changes in kidney function, proteinuria (presence of excess protein in the urine), or abnormalities detected on imaging studies.
A renal biopsy is typically performed under local anesthesia. Using imaging guidance (ultrasound or CT scan), a thin needle is inserted through the skin into the kidney to obtain a tissue sample. The sample is then sent to a pathology laboratory for analysis.
The microscopic examination of renal biopsy samples helps determine the type and severity of kidney disease, such as glomerular diseases, interstitial nephritis, or tubular disorders. This information is crucial for developing an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.